Difference between revisions of "Hadley Rille"
Jarogers2001 (talk | contribs) |
Jarogers2001 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
[[Image:As15-81-10894.jpg|left|thumb|400px|The ejecta blanket of the more recent crater [[Hadley C]] interrupts the course of the rille. Photo credit: NASA]] | [[Image:As15-81-10894.jpg|left|thumb|400px|The ejecta blanket of the more recent crater [[Hadley C]] interrupts the course of the rille. Photo credit: NASA]] | ||
| − | + | [[Apollo_15_panaromic_camera_landing_site.jpg|thumb|400px|A section of panoramic image showing Hadley Rille and the [[Apollo]] 15 landing site. The landing site may be located via the white patch of disturbed [[regolith]] in the lower left corner of the image. Photo credit: NASA.]] | |
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Preliminary Images have been loaded into this article, with fields, for ease of later modification. | Preliminary Images have been loaded into this article, with fields, for ease of later modification. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:Apollo_15_panaromic_camera_landing_site.jpg | http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:Apollo_15_panaromic_camera_landing_site.jpg | ||
Revision as of 09:54, 9 August 2008
| This article is a stub. You can help Lunarpedia by expanding it or sorting it into the correct stub subcategory. |

Also known as Rima Hadley, this rille is located within Mare Imbrium and is near the location of the Apollo 15 moon landing in an area called the Marsh of Decay (Palus Putredinus). Named for Mons Hadley, which is in turn named for John Hadley, Hadley rille begins at Béla crater and follows a generally northeast course towards Mons Hadley. It is centered at the selenological coordinates 25.0° N, 3.0° E.
{This article is unfinished. Please feel free to add content.}
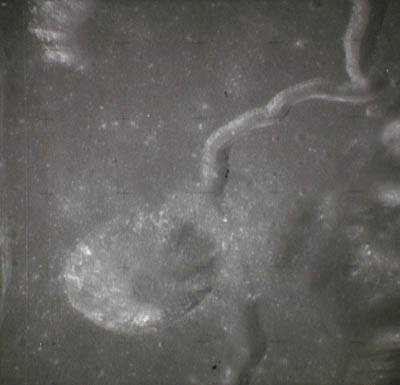
[[Apollo_15_panaromic_camera_landing_site.jpg|thumb|400px|A section of panoramic image showing Hadley Rille and the Apollo 15 landing site. The landing site may be located via the white patch of disturbed regolith in the lower left corner of the image. Photo credit: NASA.]]






