Difference between revisions of "Roof Support"
(→Supporting Regolith: reformatted table, added missing data) |
Silverwurm (talk | contribs) (Reworked page structure, significant rewording and editing of multiple entries) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | __TOC__ | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[Image:ArchDorm01.jpg|frame| [[Architecture as Mole Hills]], Standard dorm room]] | |
| − | + | ==Introduction== | |
| − | + | Structural support in lunar habitats will be quite different from earth based buildings. One primary difference is that, due to the need for lunar habitats to maintain a sizable internal pressure, most of the standard operating stresses will be internal rather than external. | |
| − | |||
| + | == Safety considerations == | ||
| − | + | Most proposals for long term lunar habitats call for the use of a thick blanket of lunar regolith to be piled atop the structure, providing protection from temperature swings, meteorite impacts, and cosmic radiation for the inhabitant, as well as any electronic equipment (see [[Architecture as Mole Hills]] and [[Architecture as Tent City]]). | |
| − | The | + | Most of the experience mankind has accumulated concerning radiation deals with nuclear radiation. The cosmic radiation encountered beyond earths magnetic field is much less understood, as it can only be replicated on earth by means of a particle accelerator. As such, the question of how much regolith is needed to protect the inhabitants is currently little more than educated guesswork, and will likely remain so until more thorough field study is performed. |
| − | + | One common estimation is to provide enough regolith to equal earths atmosphere in shielding potential. This is based on the fact that the earths magnetic field has collapsed several times in geologic history, and said collapses did not seem to have any major effect on the life on earth. As such, it is believed that the mass of earths atmosphere is by itself sufficient to guard against cosmic radiation. Assuming that air and lunar regolith have similar shielding properties according to their mass (as they do for nuclear radiation), this gives several different thicknesses, depending on what altitude is used for comparison. | |
| − | == | + | {| border=1 |
| + | ! Location !! colspan="2" | Atmospheric Pressure !! colspan="2" | Regolith Needed to Equal Atmospheric Shielding !! colspan="2" | Miniumum Internal Pressure Required | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | || kPa || psi || m || f || kPa || psi | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Sea Level || 101.3 || 14.2 || 5.4 || 17.9 || 16.9 || 2.4 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Denver a high altitude city || 84 || 12.17 || 4.5 || 14.8 || 14 || 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Mexico City, a high altitude city || 81.4 || 11.74 || 4.4 || 14.3 || 13.5 || 2 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Open airplane || 74.0 || 10.2 || 4.0 || 13 || 12.3 || 1.8 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Top of Mount Everest || 26.0 || 3.65 || 1.4 || 4.6 || 4.3 || 0.6 | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | (assuming a regolith density of 1.9 grams/cm^3 and lunar gravitation acceleration of 1.63 m/s^2) | ||
| + | |||
| + | As seen from the chart, the minimum habitat pressure level needed to support the regolith shield on pressure alone is quite low, even for sea level equivalent shielding. As such, a structure pressurized to sea level pressure (like the ISS), and covered with enough regolith equal sea level radiation shielding would have a large net force pushing outward. The reason for this is that, though the regolith piled atop the structure is the same mass per unit area as earths atmosphere would be, lunar gravity is only around 1/6 of earths, resulting in much less force pushing downward, but the same pressure pushing upward. If the same structure was constructed in earth-like gravity (but still in a vacuum), the pressure would be equal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | As a result, lunar habitat functioning under normal parameters would not require any internal support for its main structure, as the internal forces are greater. A lunar habitat could therefor be essentially a giant, reinforced balloon, covered in lunar regolith. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Depressurization=== | ||
| + | One safety consideration for such a structure is to plan for operation in case of pressure loss, also known as a blow out. Some mechanism of coping with a blow out would be required. | ||
| + | |||
| + | One method of dealing with a blowout is to make the outer structure sufficiently strong that it will not only keep in the pressure under normal conditions, but will also hold its own in a depressurized state. As seen in the chart, a structure capable of supporting a sea level equivalent regolith shield under depressurized conditions would be subject to just under 3 psi of pressure across its roof. This is approximately equivalent to designing an earthbound structure capable of maintaining twice atmospheric pressure under normal conditions, and standard atmospheric pressure six feet underwater in an emergency. A [[steel]] or [[titanium]] structure could be made sufficiently strong to withstand these forces, as could a properly designed [[Sintered Brick Construction|lunar brick]] structure reinforced with steel cable. | ||
| − | + | A structure which was supported only by internal pressure would require additional mechanisms to ensure the safety of its inhabitants in case of a blowout. One way of coping with this is to compartmentalize the structure, or in other words, design it so that separate areas could be sealed off if needed, so that a breach in one area would not affect the entire habitat. An additional safety measure that could be installed is a series of gas tanks linked to different areas of the habitat. In the event of a breach, gas could be fed in to maintain the pressure in the affected area long enough to evacuate it. | |
| − | + | It has been suggested that a structure incapable of holding its own in a depressurized state would need to be designed to allow a person wearing an environmental suit enough clearance to crawl to safety even if a second person is lying immobile in the evacuation path. It has been further suggested that this would lead to small rooms being prevalent in these types of structures, as they are much easier to reinforce against collapse. As such, building large rooms in a lunar environment would require the use of structures that do not require internal pressurization to remain standing. | |
| + | ==Pressure Considerations== | ||
| − | |||
One of the most important considerations in the design of a lunar settlement will be the internal air pressure. | One of the most important considerations in the design of a lunar settlement will be the internal air pressure. | ||
| − | + | ===High Pressure=== | |
High air pressure, that is Earth normal 101 kpa (14.2 PSI, makes the living space more Earth like. People and plants accommodate to living on the Moon easily and food is easy to cook. | High air pressure, that is Earth normal 101 kpa (14.2 PSI, makes the living space more Earth like. People and plants accommodate to living on the Moon easily and food is easy to cook. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 56: | ||
But, spacesuits must be at low pressure for the joints to work with acceptable amounts of efforts. Any time a persons moves from a high pressure to a low pressure environment, you risk nitrogen forming bubbles in your blood; a conditions called the bends. For the body to accommodate from normal air pressure to a low spacesuit pressure can take as long as an overnight stay in a low pressure chamber. | But, spacesuits must be at low pressure for the joints to work with acceptable amounts of efforts. Any time a persons moves from a high pressure to a low pressure environment, you risk nitrogen forming bubbles in your blood; a conditions called the bends. For the body to accommodate from normal air pressure to a low spacesuit pressure can take as long as an overnight stay in a low pressure chamber. | ||
| − | + | ===Low Pressure=== | |
Low air pressure, with adequate oxygen content, allows the human body to accommodation to spacesuit pressures in only a few minutes or just seconds in an emergency. Ranges from 74 kPa (10.2 psi) down to 33.5 kpi (4.7 psi) have been discussed for lunar settlements. The human body will simply never fully accommodate pressures below about 30 kPascal (4.2 psi). | Low air pressure, with adequate oxygen content, allows the human body to accommodation to spacesuit pressures in only a few minutes or just seconds in an emergency. Ranges from 74 kPa (10.2 psi) down to 33.5 kpi (4.7 psi) have been discussed for lunar settlements. The human body will simply never fully accommodate pressures below about 30 kPascal (4.2 psi). | ||
| Line 46: | Line 70: | ||
Also low air pressure will not support as thick a layer of protecting regolith over inflated buildings. | Also low air pressure will not support as thick a layer of protecting regolith over inflated buildings. | ||
| − | + | ===Supporting Regolith=== | |
Here are some of present ideas for lunar settlement air pressures and how much regolith they will support: | Here are some of present ideas for lunar settlement air pressures and how much regolith they will support: | ||
| Line 93: | Line 117: | ||
It is important to note that the internal pressure inside a living area has plenty of force to support a substantial thickness of lunar regolith above it for radiation and thermal shielding even if low pressures are used. | It is important to note that the internal pressure inside a living area has plenty of force to support a substantial thickness of lunar regolith above it for radiation and thermal shielding even if low pressures are used. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 02:21, 2 September 2011
Contents
Introduction
Structural support in lunar habitats will be quite different from earth based buildings. One primary difference is that, due to the need for lunar habitats to maintain a sizable internal pressure, most of the standard operating stresses will be internal rather than external.
Safety considerations
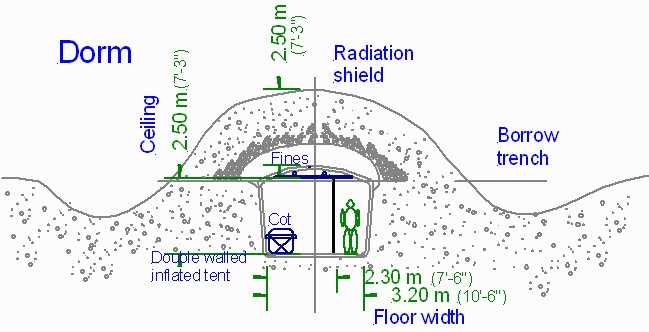
Most proposals for long term lunar habitats call for the use of a thick blanket of lunar regolith to be piled atop the structure, providing protection from temperature swings, meteorite impacts, and cosmic radiation for the inhabitant, as well as any electronic equipment (see Architecture as Mole Hills and Architecture as Tent City).
Most of the experience mankind has accumulated concerning radiation deals with nuclear radiation. The cosmic radiation encountered beyond earths magnetic field is much less understood, as it can only be replicated on earth by means of a particle accelerator. As such, the question of how much regolith is needed to protect the inhabitants is currently little more than educated guesswork, and will likely remain so until more thorough field study is performed.
One common estimation is to provide enough regolith to equal earths atmosphere in shielding potential. This is based on the fact that the earths magnetic field has collapsed several times in geologic history, and said collapses did not seem to have any major effect on the life on earth. As such, it is believed that the mass of earths atmosphere is by itself sufficient to guard against cosmic radiation. Assuming that air and lunar regolith have similar shielding properties according to their mass (as they do for nuclear radiation), this gives several different thicknesses, depending on what altitude is used for comparison.
| Location | Atmospheric Pressure | Regolith Needed to Equal Atmospheric Shielding | Miniumum Internal Pressure Required | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kPa | psi | m | f | kPa | psi | |
| Sea Level | 101.3 | 14.2 | 5.4 | 17.9 | 16.9 | 2.4 |
| Denver a high altitude city | 84 | 12.17 | 4.5 | 14.8 | 14 | 2 |
| Mexico City, a high altitude city | 81.4 | 11.74 | 4.4 | 14.3 | 13.5 | 2 |
| Open airplane | 74.0 | 10.2 | 4.0 | 13 | 12.3 | 1.8 |
| Top of Mount Everest | 26.0 | 3.65 | 1.4 | 4.6 | 4.3 | 0.6 |
(assuming a regolith density of 1.9 grams/cm^3 and lunar gravitation acceleration of 1.63 m/s^2)
As seen from the chart, the minimum habitat pressure level needed to support the regolith shield on pressure alone is quite low, even for sea level equivalent shielding. As such, a structure pressurized to sea level pressure (like the ISS), and covered with enough regolith equal sea level radiation shielding would have a large net force pushing outward. The reason for this is that, though the regolith piled atop the structure is the same mass per unit area as earths atmosphere would be, lunar gravity is only around 1/6 of earths, resulting in much less force pushing downward, but the same pressure pushing upward. If the same structure was constructed in earth-like gravity (but still in a vacuum), the pressure would be equal.
As a result, lunar habitat functioning under normal parameters would not require any internal support for its main structure, as the internal forces are greater. A lunar habitat could therefor be essentially a giant, reinforced balloon, covered in lunar regolith.
Depressurization
One safety consideration for such a structure is to plan for operation in case of pressure loss, also known as a blow out. Some mechanism of coping with a blow out would be required.
One method of dealing with a blowout is to make the outer structure sufficiently strong that it will not only keep in the pressure under normal conditions, but will also hold its own in a depressurized state. As seen in the chart, a structure capable of supporting a sea level equivalent regolith shield under depressurized conditions would be subject to just under 3 psi of pressure across its roof. This is approximately equivalent to designing an earthbound structure capable of maintaining twice atmospheric pressure under normal conditions, and standard atmospheric pressure six feet underwater in an emergency. A steel or titanium structure could be made sufficiently strong to withstand these forces, as could a properly designed lunar brick structure reinforced with steel cable.
A structure which was supported only by internal pressure would require additional mechanisms to ensure the safety of its inhabitants in case of a blowout. One way of coping with this is to compartmentalize the structure, or in other words, design it so that separate areas could be sealed off if needed, so that a breach in one area would not affect the entire habitat. An additional safety measure that could be installed is a series of gas tanks linked to different areas of the habitat. In the event of a breach, gas could be fed in to maintain the pressure in the affected area long enough to evacuate it.
It has been suggested that a structure incapable of holding its own in a depressurized state would need to be designed to allow a person wearing an environmental suit enough clearance to crawl to safety even if a second person is lying immobile in the evacuation path. It has been further suggested that this would lead to small rooms being prevalent in these types of structures, as they are much easier to reinforce against collapse. As such, building large rooms in a lunar environment would require the use of structures that do not require internal pressurization to remain standing.
Pressure Considerations
One of the most important considerations in the design of a lunar settlement will be the internal air pressure.
High Pressure
High air pressure, that is Earth normal 101 kpa (14.2 PSI, makes the living space more Earth like. People and plants accommodate to living on the Moon easily and food is easy to cook.
But, spacesuits must be at low pressure for the joints to work with acceptable amounts of efforts. Any time a persons moves from a high pressure to a low pressure environment, you risk nitrogen forming bubbles in your blood; a conditions called the bends. For the body to accommodate from normal air pressure to a low spacesuit pressure can take as long as an overnight stay in a low pressure chamber.
Low Pressure
Low air pressure, with adequate oxygen content, allows the human body to accommodation to spacesuit pressures in only a few minutes or just seconds in an emergency. Ranges from 74 kPa (10.2 psi) down to 33.5 kpi (4.7 psi) have been discussed for lunar settlements. The human body will simply never fully accommodate pressures below about 30 kPascal (4.2 psi).
At low pressures you can use 100% oxygen which greatly simplifies the entire life support system. Testing this type of system is very dangerous and has resulted in two serious fires. The key safety concept is that if the partial pressure of oxygen exceeds Earth normal of 22 kPascal (3.0 psi) then substancial fire control efforts are required.
The long term health effects of low pressure are not fully known for people or for plants. Any agricultural areas may need additional CO2, humidity, and nitrogen compared the people living areas.
Low pressure also saves the cost of shipping a large mass of bulk nitrogen from Earth. This could be a very important cost consideration in early lunar settlements.
Water boils at such a low temperature at low atmospheric pressure that cooking is difficult. You simply cannot get things hot enough to really taste right. A cup of tea that you can stir with your finger is simply not worth drinking.
Also low air pressure will not support as thick a layer of protecting regolith over inflated buildings.
Supporting Regolith
Here are some of present ideas for lunar settlement air pressures and how much regolith they will support:
| Pressure | Boiling Point Of Water | Regolith Needed to Equal Atmospheric Shielding | Maximum Regolith Supported | Comment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kPa | psi | °C | °F | m | m | |
| 101.3 | 14.2 | 100 | 212 | 5.4 | 32 | Sea Level, ISS body |
| 84 | 12.17 | 95 | 203 | 4.5 | 27 | Denver, a high altitude city |
| 81.4 | 11.74 | 94 | 201 | 4.3 | 26 | Mexico City, a high altitude city |
| 74.0 | 10.2 | 92 | 197 | 4.0 | 24 | Open airplane, ISS ports |
| 59.1 | 8.3 | 86 | 187 | 3.2 | 19 | ISS spacesuit |
| 33.5 | 4.7 | 72 | 162 | 1.8 | 10 | Apollo spacesuit |
| 30.6 | 4.3 | 70 | 158 | 1.6 | 9.9 | Shuttle spacesuit |
| 26.0 | 3.65 | 66 | 152 | 1.4 | 8.4 | Top of Mount Everest |
| 10.0 | 1.5 | 46 | 115 | 0.5 | 3.2 | 1/10 Atm, 16,000 m, unconscious in 10 sec |
The Regolith Shield column shows how much lunar regolith is needed to provide radiation shielding equivalent to the air above your head at these locations on Earth. The Regolith Support column shows how much lunar regolith can be supported on the Moon by that level of internal pressure.
These calculations are based on the following parameters:
| density of packed regolith | 1.9 | g/cm^3 | Used for this calculation |
| density of loose regolith | 1.5 | g/cm^3 | just poured in a pile |
| Lunar gravity | 1.63 | m/s^2 | about 1/6 Earth |
| Human body temperature | 37.0 | C | 98.6 F |
It is important to note that the internal pressure inside a living area has plenty of force to support a substantial thickness of lunar regolith above it for radiation and thermal shielding even if low pressures are used.
| Hazards |
|---|






