Radiation Problem
The Radiation Problem when living on the Moon
The Earth provides two types of radiation shielding critical for life: atmospheric mass and magnetic field. The Moon has neither type. On the Moon, our architecture must provide all our shielding, see Architecture List.
Protection Provide by Earth
The Earth protects us and we must copy that protection on the Moon.
The Mass of the Atmosphere
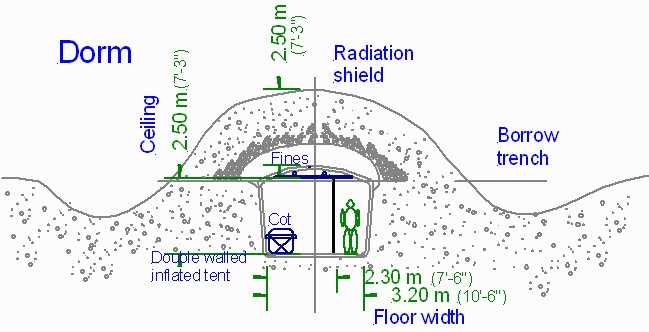
The first shield is simply the mass of the atmosphere which simply blocks radiation. The Earth's atmosphere has a mass equivalent to about 32 feet of water. It will take a layer of at least two meters of lunar regolith to match this mass and more is better. A blanket of two meters of regolith provides about the mass protection for a person living in a high altitude city like Denver or Mexico City.
The Earth's magnetic field
The second shield is the Earth's magnetic field. This field diverts most of the radiation coming from the Sun into the Van Allen belts. The Moon has no such field and is, for the large part, outside the Earth's field. There is no practical way to generate such a field around a lunar settlement.
The Solar Challange
Much of the radiation problem comes from the sun.
Corona Mass Ejections
The Sun has major storms, called Corona Mass Ejections (CME), which dump large amounts of radiation out into space. These space weather storms are associated with large sun spots and can do a great deal of damage to utilities on Earth, and to our satellites. We have a satellite system to monitor for possible danger which will be very important in our return to the moon. These storms hit the Moon from 0 to 5 times a year.
Direct Radiation
The storms provide two distinct forms of radiation danger. First they put out a great surge of high energy particles that expand out at a substantial fraction of the speed of light. Our warning system will provide only 30 to 40 minutes of warning for this danger. Anyone caught out on the surface will be subject to a severe health threat. This danger only lasts a few hours.
This form of radiation is a special problem. It actually generates secondary radiation in this first layer of mass shielding. To protect against the high energy particles and the secondary particles they generate takes six to ten meters of regolith. Thicknesses in between are not much help.
Ionized Gas
The second form of solar radiation is the mass of ionized gas thrown out by the CME. Composed mostly of ionized hydrogen these clouds have a mass equivalent to a large mountain and are the source of the volatiles that may be mined from the lunar regolith. These storms follow a curved path so the ones that hit the Moon are not the ones associated with direct radiation storms that put us in danger.
The good news is that we will have 24 to 48 hours warning about this form of radiation storm. They will then last 24 to 72 hours. These will be very dangerous for people doing outside operations but the regolith shield is much more effective inside.
Radon Gas
Another source of dangerous radiation is the radon gas that is created in the decay of trace amounts of uranium found naturally in lunar rocks. This gas is very heavy and concentrates in low areas. This type of radiation is easily stopped by even a thin layer of material, but radon is carcinogenic if ingested directly into the body.
If lunar habitats are partially buried to provide protection from solar radiation, they must be completely sealed to prevent radon from seeping up from below. The floor membranes are particularly difficult to maintain because they are subject to damage from furniture legs and foot wear.
Radon has also been detected from lunar outgassing events.
References
- [The Ions are Coming!] discusses the the monitoring of solar electrons to predict more problematic radiation.
| Hazards |
|---|