Difference between revisions of "Volatiles"
(→Gaseous Byproducts: typo) |
|||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[ | + | [[File:Sandworm vectorized 07.svg|thumb|400px|Sandworm proposal by [[User:Jriley|Tom Riley]], Side View]] |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Long term lunar settlement, not to mention going on to Mars, will depend on successful extraction of volatile substances from the Moon. | + | ==Volatile Recovery on the Moon== |
| + | Long term lunar settlement, not to mention going on to Mars, will depend on successful extraction of volatile substances from the Moon. | ||
| + | ===Volatiles, The Key to Settlement=== | ||
| + | The primary resource of value to humans on the Moon is the volatile components found in the [[regolith]]. These are all the components that are gases at room temperature. Most of the volatiles have been deposited in the top layers of the Moon's surface by the [[solar wind]] over geologic time. A notable exception to this is [[Argon]]. the concentration of Argon in lunar soil is much higher than found in the solar wind, so must come from a different source. Especially, the isotope Argon-40. It is presently believed that the Argon-40 comes from radioactive decay of [[Potassium]] deep within the lunar mantle or core, and that the Argon-40 seeps out to the surface via fissures. This vented Argon enters the lunar atmosphere; then the Argon is implanted into the regolith by interactions with ions from the solar wind. | ||
| − | + | The volatiles contain material useful for rocket fuel, reaction mass, for making air to breath, and for industrial operations. | |
| − | The | + | The various constituents of the volatiles vary from place to place on the Moon. Access to a mining area with high abundances will be a major concern for any settlement site. |
| − | + | Dr. Harrison Schmitt in his lectures at University of Wisonsin provides some links on their page page with data on abundance of luanr volatile components: | |
| + | <ref>[http://fti.neep.wisc.edu/neep602/lecture13.html NEEP602 Course Notes (Fall 1996) Resources from Space] Lecture #13: It's only a gassy Moon! | ||
| + | Title: Resources of the Moon: Solar Wind/Cosmic Ray Derived</ref>. | ||
| − | + | That web page in turn has additional references which talk about the proportions of volatiles and their respective release temperatures. | |
| − | ( | + | The major components (when regolith heated to 700 deg C) are: |
| − | + | (in order of abundance and compared to the abundance of Helium-3 by mass) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [[Hydrogen]]--------(6,100 times Helium-3 by mass) | |
| + | * [[Water]] ----------(3,300 times Helium-3 by mass) | ||
| + | * [[Helium4]] with a trace amount of [[Helium3] one part in 3,100 by mass | ||
| + | * [[Carbon Monoxide]]-(1,900 times Helium-3 by mass) | ||
| + | * [[Carbon Dioxide]]--(1,700 times Helium-3 by mass) | ||
| + | * [[Methane]]---------(1,600 times Helium-3 by mass) | ||
| + | * [[Nitrogen]]--------(500 times Helium-3 by mass) | ||
| + | * [[Argon]] | ||
| + | * Other Inert gases, [[Neon]] and [[Radon]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | When the regolith is heated to 900 deg C, a considerable quantity of sulfur compounds is released, including [[Hydrogen Sulfide]] and [[Sulfur Dioxide]] | ||
| + | <ref>[http://fti.neep.wisc.edu/neep602/LEC13/IMAGES/inventory.JPG] Inventory of Lunar Volatiles in first three meters of regolith (note log scale)</ref><ref>[http://fti.neep.wisc.edu/neep602/9301/node2.html#SECTION00020000000000000000] Concentrations of Various Volatiles in Apollo 11 Regolith</ref>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This chart is a very interesting depiction of the valitiles available when regolith is heated to 700 Deg c: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://fti.neep.wisc.edu/neep602/LEC13/IMAGES/volatiles.JPG Inventory of Lunar Volatiles relative to the production of one tonne of helium-3 ] | ||
===Apollo Regolith Testing=== | ===Apollo Regolith Testing=== | ||
| − | |||
Regolith samples from Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 were returned to Earth and analyzed for the volatiles they emitted when heated in a vacuum. | Regolith samples from Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 were returned to Earth and analyzed for the volatiles they emitted when heated in a vacuum. | ||
| − | + | ||
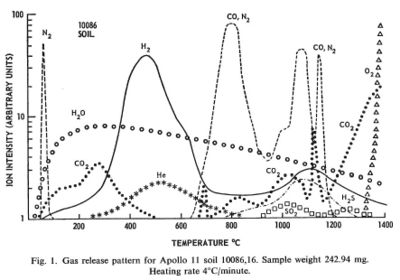
[[Image:Apollo11Soil.jpg|right|thumb|400px|Apollo 11 gas release from soil sample 10086,16]] | [[Image:Apollo11Soil.jpg|right|thumb|400px|Apollo 11 gas release from soil sample 10086,16]] | ||
| − | + | ||
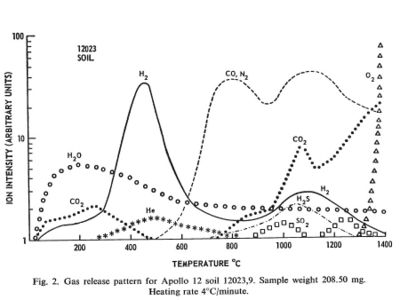
[[Image:Apollo12Soil.jpg|right|thumb|400px|Apollo 12 gas release from soil sample 12023,9]] | [[Image:Apollo12Soil.jpg|right|thumb|400px|Apollo 12 gas release from soil sample 12023,9]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The regolith samples were exposed to Earth air and may have picked up some volatiles in transport. Lunar regolith is regularly subject to heating from the sun to at least 150 C. Any volatiles coming out below that temperature was taken to be from Earth. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Between the temperatures of 150 C and 700 C substantial amounts of hydrogen, water, carbon dioxide, and helium came off the samples. In this temperature range the molecules must have been adsorbed on the surface of crystal grains and not bound in chemical compounds. These temperatures are probably achievable by the use of concentrated solar energy. | ||
| − | + | Between the temperatures of 700 C and 1400 C additional volatile materials come off including substantial amount so nitrogen, carbon monoxide, [[hydrogen sulfide]], and finally oxygen. These volatiles probably represent the breakdown of more complex compounds. These temperatures are routinely achieved in industrial processes on Earth. The volatile output can probably be increased by providing a reducing atmosphere, such as hot hydrogen, and by the presence of a catalyst, such as [[platinum]]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Between the temperatures of 700 C and 1400 C additional volatile materials come off including substantial amount so nitrogen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and finally oxygen. | ||
[[http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1971LPSC....2.1351G]] Gibson, E. K., Jr.; Johnson, S. M., Thermal Analysis-Inorganic Gas Release of Lunar Samples | [[http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1971LPSC....2.1351G]] Gibson, E. K., Jr.; Johnson, S. M., Thermal Analysis-Inorganic Gas Release of Lunar Samples | ||
| − | ===Processing Regolith=== | + | ===Processing Regolith=== |
| + | A major enterprise of any lunar settlement will be the processing of lunar regolith for volatile scavenging. Once the volatile gas mix has been extracted from the regolith, then fractional distillation can be used to separate out the different chemical constituents which have different boiling points. In one proposal, called the [[Sandworms|Sandworm]], a very large vehicle would crawl across the landscape milling out a trench three meters deep and up to 23 meters wide. Some of these trenches could then be used as sites for buildings. Other proposals include smaller vehicle processing or the use of collection vehicles or other means for bringing regolith to a stationary processing facility. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The primary uses of the volatiles are: | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Lunar use for breathable atmosphere | ||
| + | * Earth orbit and interplanetary Spaceship atmosphere | ||
| + | * Rocket fuel and oxidizer, and reaction mass (esp Methane and Ammonia) | ||
| + | * Industrial stocks | ||
| + | * Helium-3 for the Earth market | ||
| + | * water for use on the Moon and in Earth orbit and interplanetary spacecraft | ||
| − | + | It is necessary to process only a few tens of kilograms of regolith a shift to replace atmosphere loses in an early small station. A much higher rate of processing will be needed to produce air to grow the settlement and to produce fuel and oxidizer for return flights to the Earth or for trips on to Mars. | |
| − | + | To supply the present global demand of Helium-3 would require processing 30 tons per hour. | |
| − | + | Volatiles are released by heating the regolith. Different volatiles are released at different temperatures: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * 300 deg C --- some Helium and Hydrogen | |
| + | * 500 deg C --- CO2 and CO | ||
| + | * 675 deg C --- more CO2 | ||
| + | * 700 deg C --- more CO, Nitrogen, all remaining H2 and He | ||
| + | * 900 to 1,000 deg C -- Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfur Dioxide | ||
| + | * 1,100 to 1,200 deg C -- basalt melts | ||
| + | * 1,455 deg C -- Nickel melts | ||
| + | * 1,538 deg C -- Iron melts | ||
| + | A process to separate the voltile consitutents could be: | ||
| − | + | * 1) heat to 400 deg C, collect the H and He | |
| + | (then fractionally distill to separate H from He) | ||
| + | * 2) heat to 600 deg C, collect CO and CO2 | ||
| + | (then fractionally distill to separate CO from CO2) | ||
| + | * 3) heat to 675 deg C to collect more CO2 | ||
| + | * 4) heat to 700 degC to collect CO, H, He, N | ||
| + | (then fractionally distill to separate the consituents) | ||
| + | * 5) Heat to 950 deg C and collect H2S and SO2 | ||
| + | (then fractionally distill to separate H2S from SO2) | ||
| + | * 6) heat to 1,200 degC , separate remaining iron particles, cast the basalt into useful components, then cool slowly to anneal. | ||
| − | + | Fractional distillaiton would best be performed during the luanr night when ambient temperature falls, reducing the energy needed to condense the various gases. | |
| − | Helium 3 is | + | ===Helium 3, Special Considerations=== |
| + | [[Helium 3]] is a special case. As detailed in [[Harrison Schmitt]]'s book "Return to the Moon", it is the only lunar resource worth shipping back to the surface of the Earth at this time. In the long term, it could be used in fusion power plants on Earth as a source of clean, non-carbon energy. This type of power plant is currently under development, but is not yet near commercial operation. | ||
| + | Helium 3 is very rare on Earth and only a minor component of the lunar regolith volatiles. To refine enough to feed a power plant for a medium size city would require processing regolith at the rate of about 50 tons an hour. The scale of processing needed is directly reflected in the large scale of the proposed [[Sandworms|Sandworm]]. A commercial operation of this size on Earth would not be considered a very large facility, but we are talking about the Moon. | ||
| − | === | + | ====Chronic shortage of Helium-3 isotope could be resolved by mining lunar regolith==== |
| − | + | Even though nuclear fusion is not yet realized, there is already a strong market for Helium3 on Earth which might be enough to support a start-up robotic mining operation. Refer to the detailed analysis at this link: [http://www.lunarpedia.org/index.php?title=Helium#Chronic_shortage_of_Helium-3_isotope_could_be_resolved_by_mining_lunar_regolith] | |
| − | The magnetically beneficiated material is valuable as an ore concentrate and can be robotically handled. It is placed in a [[pressure vessel]] with an atmosphere of [[hydrogen]], which is the largest component of the volatile extraction. The vessel is then solar heated to about 1200 C for 20 minutes. The result is that the ore is reduced to iron, [[titanium dioxide]], and [[water]]. The water comes off as a vapor and can be electrically split into hydrogen and oxygen. This process appears to be the least energetic approach for obtaining substantial amounts of water and oxygen on the Moon. | + | ===Cooking out the O2=== |
| − | + | The easiest source of oxygen on the Moon is a [[Titanium]]-[[Iron]]-[[Oxygen]] mineral called [[ilmenite]] (FeTiO3) which can be processed via a [[ilmenite reduction|reduction reaction]]. It is a straight forward process to [[magnetically]] [[beneficiate]] this mineral while handling the [[regolith]] [[fines]]. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The magnetically beneficiated material is valuable as an ore concentrate and can be robotically handled. It is placed in a [[pressure vessel]] with an atmosphere of [[hydrogen]], which is the largest component of the volatile extraction. The vessel is then solar heated to about 1200 C for 20 minutes. The result is that the ore is reduced to iron, [[titanium dioxide]], and [[water]]. The water comes off as a vapor and can be electrically split into hydrogen and oxygen. This process appears to be the least energetic approach for obtaining substantial amounts of water and oxygen on the Moon. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | =====Byproducts===== | ||
| + | ======Solid Byproducts====== | ||
| + | The solids left from this process will remain a good titanium and iron ore. This material may become a valuable asset for later settlers and can be used to make [[ceramic]] tiles for flooring or as feedstock for other chemical processes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ======Gaseous Byproducts====== | ||
After the hydrogen has been consumed, the remaining volatiles will be mostly Helium and Argon. The Argon can be removed by fractionally distilling the gas mixture. The Argon can be used as propellant for electric propulsion thrusters (ion drives). The Helium can be separated into the two main isotopes by methods described elsewhere. The isotope [[Helium 3]] is potentially useful as fuel for nuclear fusion reactors. | After the hydrogen has been consumed, the remaining volatiles will be mostly Helium and Argon. The Argon can be removed by fractionally distilling the gas mixture. The Argon can be used as propellant for electric propulsion thrusters (ion drives). The Helium can be separated into the two main isotopes by methods described elsewhere. The isotope [[Helium 3]] is potentially useful as fuel for nuclear fusion reactors. | ||
| − | ===Ice at the Poles=== | + | ===Ice at the Poles=== |
| + | Two missions so far ([[Clementine]] and [[Lunar Prospector]]) have produced evidence for hydrogen in the polar regions of the Moon. The present theory is that it is in the form of water ice particles mixed with the [[regolith]] in permanently shadowed [[craters]]. The amount and properties of this resource are not currently known, but we soon will have definitive data from the [[Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter]] mission ([[LRO]]) by 2010. | ||
| − | + | Even if substantial amounts of water are present in the polar traps, it may be very difficult to mine. The very nature of the traps is that they have no access to [[solar power]] at all and they are at the bottoms of deep craters. For a settlement to take advantage of this resource it will need to be on near by high ground and work the area robotically. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | Even if substantial amounts of water are present in the polar traps, it may be very difficult to mine. The very nature of the traps is that they have no access to [[solar power]] at all and they are at the bottoms of deep craters. For a settlement to take advantage of this resource it will need to be on near by high ground and work the area robotically. | + | This will be very difficult work at the [[cryogenic]] temperatures in the traps. It is not clear whither simply working the sunlit uplands, with plenty of solar power but only a trace of [[volatiles]], is not the better idea. We will know soon. |
| − | |||
| − | This will be very difficult work at the [[cryogenic]] temperatures in the traps. It is not clear whither simply working the sunlit uplands, with plenty of solar power but only a trace of [[volatiles]], is not the better idea. We will know soon. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | ===Outgassing of Volatiles=== | ||
There are some sites on the Moon where natural release of volatiles via [[Lunar outgassing|outgassing]] of volatiles has been observed. In particular, the crater [[Aristarchus]] is well known. Outgassing sites would be attractive locations for settlements<ref>[http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/070730_gassy_moon.html Lunar Flash Mystery Solved: Moon Just Passing Gas] By David Powell posted: 30 July 2007</ref>. | There are some sites on the Moon where natural release of volatiles via [[Lunar outgassing|outgassing]] of volatiles has been observed. In particular, the crater [[Aristarchus]] is well known. Outgassing sites would be attractive locations for settlements<ref>[http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/070730_gassy_moon.html Lunar Flash Mystery Solved: Moon Just Passing Gas] By David Powell posted: 30 July 2007</ref>. | ||
| − | + | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | ---- | + | |
| − | + | [[Category:Mining]] | |
| − | [[Category:Mining]] | + | [[Category:Selenology]] |
| − | [[Category:Selenology]] | + | [[Category:Chemistry]] |
| − | [[Category:Chemistry]] | + | [[Category:ISRU]] |
| − | [[Category:ISRU]] | + | [[Category:Stories]] |
| − | [[Category:Stories]] | + | [[Category:Business]] |
| − | [[Category:Business]] | ||
[[Category:Gases]] | [[Category:Gases]] | ||
Latest revision as of 05:49, 4 April 2016
Contents
Volatile Recovery on the Moon
Long term lunar settlement, not to mention going on to Mars, will depend on successful extraction of volatile substances from the Moon.
Volatiles, The Key to Settlement
The primary resource of value to humans on the Moon is the volatile components found in the regolith. These are all the components that are gases at room temperature. Most of the volatiles have been deposited in the top layers of the Moon's surface by the solar wind over geologic time. A notable exception to this is Argon. the concentration of Argon in lunar soil is much higher than found in the solar wind, so must come from a different source. Especially, the isotope Argon-40. It is presently believed that the Argon-40 comes from radioactive decay of Potassium deep within the lunar mantle or core, and that the Argon-40 seeps out to the surface via fissures. This vented Argon enters the lunar atmosphere; then the Argon is implanted into the regolith by interactions with ions from the solar wind.
The volatiles contain material useful for rocket fuel, reaction mass, for making air to breath, and for industrial operations.
The various constituents of the volatiles vary from place to place on the Moon. Access to a mining area with high abundances will be a major concern for any settlement site.
Dr. Harrison Schmitt in his lectures at University of Wisonsin provides some links on their page page with data on abundance of luanr volatile components: [1].
That web page in turn has additional references which talk about the proportions of volatiles and their respective release temperatures.
The major components (when regolith heated to 700 deg C) are:
(in order of abundance and compared to the abundance of Helium-3 by mass)
- Hydrogen--------(6,100 times Helium-3 by mass)
- Water ----------(3,300 times Helium-3 by mass)
- Helium4 with a trace amount of [[Helium3] one part in 3,100 by mass
- Carbon Monoxide-(1,900 times Helium-3 by mass)
- Carbon Dioxide--(1,700 times Helium-3 by mass)
- Methane---------(1,600 times Helium-3 by mass)
- Nitrogen--------(500 times Helium-3 by mass)
- Argon
- Other Inert gases, Neon and Radon
When the regolith is heated to 900 deg C, a considerable quantity of sulfur compounds is released, including Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfur Dioxide [2][3].
This chart is a very interesting depiction of the valitiles available when regolith is heated to 700 Deg c:
Inventory of Lunar Volatiles relative to the production of one tonne of helium-3
Apollo Regolith Testing
Regolith samples from Apollo 11 and Apollo 12 were returned to Earth and analyzed for the volatiles they emitted when heated in a vacuum.
The regolith samples were exposed to Earth air and may have picked up some volatiles in transport. Lunar regolith is regularly subject to heating from the sun to at least 150 C. Any volatiles coming out below that temperature was taken to be from Earth.
Between the temperatures of 150 C and 700 C substantial amounts of hydrogen, water, carbon dioxide, and helium came off the samples. In this temperature range the molecules must have been adsorbed on the surface of crystal grains and not bound in chemical compounds. These temperatures are probably achievable by the use of concentrated solar energy.
Between the temperatures of 700 C and 1400 C additional volatile materials come off including substantial amount so nitrogen, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, and finally oxygen. These volatiles probably represent the breakdown of more complex compounds. These temperatures are routinely achieved in industrial processes on Earth. The volatile output can probably be increased by providing a reducing atmosphere, such as hot hydrogen, and by the presence of a catalyst, such as platinum.
[[3]] Gibson, E. K., Jr.; Johnson, S. M., Thermal Analysis-Inorganic Gas Release of Lunar Samples
Processing Regolith
A major enterprise of any lunar settlement will be the processing of lunar regolith for volatile scavenging. Once the volatile gas mix has been extracted from the regolith, then fractional distillation can be used to separate out the different chemical constituents which have different boiling points. In one proposal, called the Sandworm, a very large vehicle would crawl across the landscape milling out a trench three meters deep and up to 23 meters wide. Some of these trenches could then be used as sites for buildings. Other proposals include smaller vehicle processing or the use of collection vehicles or other means for bringing regolith to a stationary processing facility.
The primary uses of the volatiles are:
- Lunar use for breathable atmosphere
- Earth orbit and interplanetary Spaceship atmosphere
- Rocket fuel and oxidizer, and reaction mass (esp Methane and Ammonia)
- Industrial stocks
- Helium-3 for the Earth market
- water for use on the Moon and in Earth orbit and interplanetary spacecraft
It is necessary to process only a few tens of kilograms of regolith a shift to replace atmosphere loses in an early small station. A much higher rate of processing will be needed to produce air to grow the settlement and to produce fuel and oxidizer for return flights to the Earth or for trips on to Mars.
To supply the present global demand of Helium-3 would require processing 30 tons per hour.
Volatiles are released by heating the regolith. Different volatiles are released at different temperatures:
- 300 deg C --- some Helium and Hydrogen
- 500 deg C --- CO2 and CO
- 675 deg C --- more CO2
- 700 deg C --- more CO, Nitrogen, all remaining H2 and He
- 900 to 1,000 deg C -- Hydrogen Sulfide and Sulfur Dioxide
- 1,100 to 1,200 deg C -- basalt melts
- 1,455 deg C -- Nickel melts
- 1,538 deg C -- Iron melts
A process to separate the voltile consitutents could be:
- 1) heat to 400 deg C, collect the H and He
(then fractionally distill to separate H from He)
- 2) heat to 600 deg C, collect CO and CO2
(then fractionally distill to separate CO from CO2)
- 3) heat to 675 deg C to collect more CO2
- 4) heat to 700 degC to collect CO, H, He, N
(then fractionally distill to separate the consituents)
- 5) Heat to 950 deg C and collect H2S and SO2
(then fractionally distill to separate H2S from SO2)
- 6) heat to 1,200 degC , separate remaining iron particles, cast the basalt into useful components, then cool slowly to anneal.
Fractional distillaiton would best be performed during the luanr night when ambient temperature falls, reducing the energy needed to condense the various gases.
Helium 3, Special Considerations
Helium 3 is a special case. As detailed in Harrison Schmitt's book "Return to the Moon", it is the only lunar resource worth shipping back to the surface of the Earth at this time. In the long term, it could be used in fusion power plants on Earth as a source of clean, non-carbon energy. This type of power plant is currently under development, but is not yet near commercial operation.
Helium 3 is very rare on Earth and only a minor component of the lunar regolith volatiles. To refine enough to feed a power plant for a medium size city would require processing regolith at the rate of about 50 tons an hour. The scale of processing needed is directly reflected in the large scale of the proposed Sandworm. A commercial operation of this size on Earth would not be considered a very large facility, but we are talking about the Moon.
Chronic shortage of Helium-3 isotope could be resolved by mining lunar regolith
Even though nuclear fusion is not yet realized, there is already a strong market for Helium3 on Earth which might be enough to support a start-up robotic mining operation. Refer to the detailed analysis at this link: [4]
Cooking out the O2
The easiest source of oxygen on the Moon is a Titanium-Iron-Oxygen mineral called ilmenite (FeTiO3) which can be processed via a reduction reaction. It is a straight forward process to magnetically beneficiate this mineral while handling the regolith fines.
The magnetically beneficiated material is valuable as an ore concentrate and can be robotically handled. It is placed in a pressure vessel with an atmosphere of hydrogen, which is the largest component of the volatile extraction. The vessel is then solar heated to about 1200 C for 20 minutes. The result is that the ore is reduced to iron, titanium dioxide, and water. The water comes off as a vapor and can be electrically split into hydrogen and oxygen. This process appears to be the least energetic approach for obtaining substantial amounts of water and oxygen on the Moon.
Byproducts
Solid Byproducts
The solids left from this process will remain a good titanium and iron ore. This material may become a valuable asset for later settlers and can be used to make ceramic tiles for flooring or as feedstock for other chemical processes.
Gaseous Byproducts
After the hydrogen has been consumed, the remaining volatiles will be mostly Helium and Argon. The Argon can be removed by fractionally distilling the gas mixture. The Argon can be used as propellant for electric propulsion thrusters (ion drives). The Helium can be separated into the two main isotopes by methods described elsewhere. The isotope Helium 3 is potentially useful as fuel for nuclear fusion reactors.
Ice at the Poles
Two missions so far (Clementine and Lunar Prospector) have produced evidence for hydrogen in the polar regions of the Moon. The present theory is that it is in the form of water ice particles mixed with the regolith in permanently shadowed craters. The amount and properties of this resource are not currently known, but we soon will have definitive data from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter mission (LRO) by 2010.
Even if substantial amounts of water are present in the polar traps, it may be very difficult to mine. The very nature of the traps is that they have no access to solar power at all and they are at the bottoms of deep craters. For a settlement to take advantage of this resource it will need to be on near by high ground and work the area robotically.
This will be very difficult work at the cryogenic temperatures in the traps. It is not clear whither simply working the sunlit uplands, with plenty of solar power but only a trace of volatiles, is not the better idea. We will know soon.
Outgassing of Volatiles
There are some sites on the Moon where natural release of volatiles via outgassing of volatiles has been observed. In particular, the crater Aristarchus is well known. Outgassing sites would be attractive locations for settlements[4].
References
- ↑ NEEP602 Course Notes (Fall 1996) Resources from Space Lecture #13: It's only a gassy Moon! Title: Resources of the Moon: Solar Wind/Cosmic Ray Derived
- ↑ [1] Inventory of Lunar Volatiles in first three meters of regolith (note log scale)
- ↑ [2] Concentrations of Various Volatiles in Apollo 11 Regolith
- ↑ Lunar Flash Mystery Solved: Moon Just Passing Gas By David Powell posted: 30 July 2007